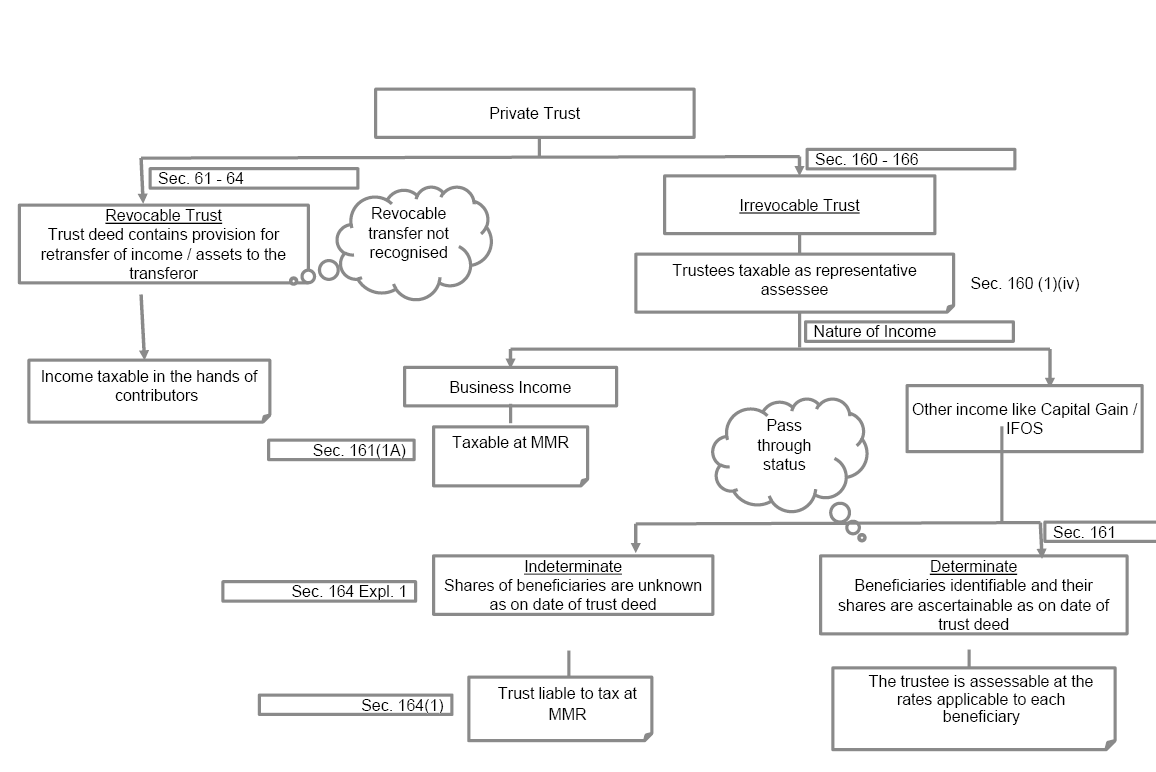
Query 1.
GST – Liability for out and out Supply
What are the GST Implications in case of dropshipping?
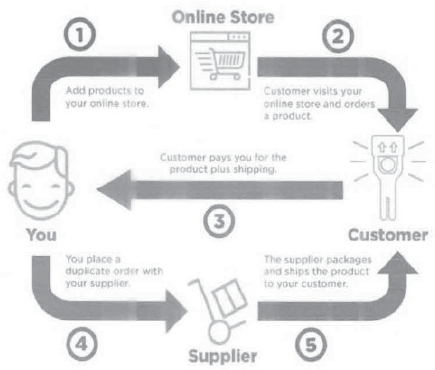
Facts of the Case:
• Online store is Shopify.com which gives support to our website which is hosted from outside India.
• All transactions are processed/done through Paypal which is an American Payment Gateway.
• Supplier is Ali Express which is from China
• Our Customers are from USA and Australia
• Material is directly shipped from China to USA/Australia
• Our cost is Material Cost + Shipping Cost + Website Expenses + Transaction Charges of Paypal
• Tax Invoice is not raised from India.
Questions:
• Whether GST is applicable in such cases of dropshipping?
• If applicable, what is the GST liability of dealer in India who is just hosting the website?
Reply
From above facts, it appears that the goods will be delivered from China to USA / Australia. Thus, goods are dealt with out of taxable territory i.e. India.
Under above circumstances, no liability arises in India under GST Act. We have AR from Maharashtra in case of Enmarol Petroleum India Pvt. Ltd. (GST ARA -53/2018-19/B-127 dated 10-10-2018)(Mah). In this case, in similar facts, it is held that no liability arises in India.
Now, there is amendment in GST Act. In Schedule III to CGST Act following entry is inserted.
“7. Supply of goods from a place in the non-taxable territory to another place in the non-taxable territory without such goods entering into India.”
Thus after 1-2-2019, it is specifically made clear that no liability in India in above facts, though otherwise supplier situated in India.
We have not understood the reference to hosting of website in India.
In facts it is mentioned that the website is hosted from outside India. Therefore, there is some confusion. However in any case, regarding goods delivered from out and out i.e. China to USA no liability in India. There appears to be no income in India from hosting of website. Therefore, no liability arises in India in respect of same.
Query 2
Now a days there are news about arrest of person by GST Authorities. Please explain, in brief, the provisions related to arrest and search/seizure?
Reply
Provisions of Inspection, Search, Seizure and Arrest
Sections 67 to 72 provides for the above aspects. The short study of above sections reveal as under:
Power of Inspection, Search and Seizure
Section 67(1) reads as under:
“67. (1) Where the proper officer, not below the rank of Joint Commissioner, has reasons to believe that––
(a) a taxable person has suppressed any transaction relating to supply of goods or services or both or the stock of goods in hand, or has claimed input tax credit in excess of his entitlement under this Act or has indulged in contravention of any of the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder to evade tax under this Act; or
(b) any person engaged in the business of transporting goods or an owner or operator of a warehouse or a godown or any other place is keeping goods which have escaped payment of tax or has kept his accounts or goods in such a manner as is likely to cause evasion of tax payable under this Act, he may authorise in writing any other officer of central tax to inspect any places of business of the taxable person or the persons engaged in the business of transporting goods or the owner or the operator of warehouse or godown or any other place.”
The section requires fulfillment of following criteria on part of department.
• Authorisation of inspection has to be given by the officer of the rank of Joint Commissioner or above.
• Authorising officer must have Reason to Believe that taxable person is:
– Suppressing any transaction; or
– Suppressing Stock in hand; or – Claiming of excess Input Tax Credit; or
– Indulging in contravention of any of the provisions of the law to evade tax; or
o transporter is keeping the goods which has escaped tax or has kept his accounts or goods in such a manneras is likely to cause evasion of tax
o operator of warehouse or godown or any other place is keeping the goods which has escaped tax or has kept his accounts or goods in such a manner as is likely to cause evasion of tax
• Authorisation should be in writing in Form No. GST INS-01, for Inspection.
• Inspection can be of Place of Business only. Place of Business has been defined in Sec. 2(85) to include godown or any other place where a taxable person stores his goods, maintain his books of account and place of agent. Accordingly, if books of account are being maintained or kept at residence of director or any other key managerial person the same shall be treated as place of business and inspection can be carried out there.
The definition of “place of business” (POB) in section 2(85) is very wide and the inspection cannot be only at regular POB but also at residence or other place, if the books etc. are being kept there.
Search / Seizure
The further extension of inspection is the search/seizure.
The said provision is contained in section 67(2) which reads as under:-
“(2) Where the proper officer, not below the rank of Joint Commissioner, either pursuant to an inspection carried out under sub-section (1) or otherwise, has reasons to believe that any goods liable to confiscation or any documents or books or things, which in his opinion shall be useful for or relevant to any proceedings under this Act, are secreted in any place, he may authorise in writing any other officer of central tax to search and seize or may himself search and seize such goods, documents or books or things:
Provided that where it is not practicable to seize any such goods, the proper officer, or any officer authorised by him, may serve on the owner or the custodian of the goods an order that he shall not remove, part with, or otherwise deal with the goods except with the previous permission of such officer:
Provided further that the documents or books or things so seized shall be retained by such officer only for so long as may be necessary for their examination and for any inquiry or proceedings under this Act.”
The Seizure, as the section suggest, is power for forceful entry/breaking open and unearthing hidden materials/records/goods etc.. The basic features of above provisions can be noted as under:
• “Authorisation of Search & Seizure has to be given by the officer of the rank of Joint Commissioner or above.
• Authorising officer must have Reason to Believe that
– Goods liable for confiscation are secreted in any place
– Books, documents or something, which is useful or relevant for proceeding under GST law, are secreted in any place.
• Authorisation should be in writing in form GST INS-01 for Search.
• In case of Seizure, Order of Seizure is to be issued in form GST INS-02.
In search & seizure proceedings goods which are liable for confiscation can only be seized. As per Sec. 130(1) of the C/SGST Act, following goods are liable for confiscation, under the law:
(i) If supply is made in contravention of any of the provisions of GST law with intention to evade payment of tax, or
(ii) If goods are not accounted for on which tax is liable to be paid or
(iii) If goods liable to tax are supplied without having applied for registration (30 days time limit is there for applying registration, from the date person becomes liable for paying tax).
Comparative Position of Inspection and Search & Seizure
|
Aspect Issue
|
Inspection – Sec. 67(1)
|
Search – Sec. 67(2)
|
|
Primary Purpose
|
Verification of transactions of supplies, stock in hand, claim of ITC & contravention of provisions of the Act to evade tax.
|
Unearthing of goods liable for confiscation or secreted books, documents or things.
|
|
Scope
|
Inspection can be done at Place of Business only.
|
Search can be done at Any Place including residence of tax payer and/ or employees.
|
|
Powers
|
Forceful action (Sealing or Break Open) cannot be adopted.
|
Seal or Break Open the door of any premises or break open any almirah, electronic devices, box, receptacle in which any goods accounts, registers or documents of the person are suspected to be concealed, where access to such premises, almirah, electronic devices, box or receptacle is denied, can be resorted.
|
|
Seizure of Goods
|
Goods cannot be seized in inspection proceedings.
|
Goods can be seized if they are liable for confiscation. If not practically possible to seize, constructive seizure can be there.
|
|
Seizure of Books of Account/Documents
|
Books/documents cannot be seized in inspection proceeding.
|
Any secreted document, books or things, which may be useful or relevant to any proceedings can be seized.
|
It can be noted that there are no specific provisions about timing of search and also period for which search can go on. These are practical issues and are required to be seen with judicial pronouncements. It can also be noted that the search etc. may be declared invalid in future. However the material seized can be used as evidence for adverse action against the concerned person.
Inspection of Business Premises
Sec. 71 of the C/SGST Act provides for access to place of business by the officers authorized by the proper officer not below the rank of Joint Commissioner. The purposes of such access to business premises may be audit, scrutiny or verification to ensure interest of the revenue. In such cases person in-charge of place of business shall be under an obligation to make available books of account, financial statements, income tax audit report (if any), cost audit report under companies law (if any) and any other relevant records for examination and verification. These powers can be exercised by auditor appointed u/s. 66 as well. It is pertinent to note that the term audit as defined in sec. 2(13) of C/SGST Act includes examination and verification of records and documents maintained under provisions of GST law or under any other law for the time being in force, that means authorized officer or special auditor may ask for records which are mandated to be kept under GST law and also under any other law. For example, in case of mining company, records made under mining law can be asked for and in case of a hotel the records of guest (or guest register) can be asked for verification and examination to ascertain proper disclosure as regards to supply of goods or services and payment of taxes thereon.
Powers of Arrest
One of the substantive power given under GST Act is about arrest. Normally, the tax authorities cannot directly arrest any person. They have to file compliant to the police and police can take necessary action.
Under VAT provisions there were no such powers. Now under GST, these powers are given. The scrutiny of section 69 reveals as under:
Section 69 empowers officer to arrest of person. Arrest is considered as strongest enforcement right as it breaches fundamental right of a person of freedom. The authorisation to arrest can be issued by Commissioner only, that too when he has reason to believe that such person has committed specified offence which is punishable u/s. 132(1) (i)/ (ii) or Sec. 132(2) of the C/SGST Act. Specified offences are:
a) Supply of goods or services without issue of invoice, with the intention to evade tax.
b) Issue of invoice without supply of goods or services which leads to wrongful availment of ITC or refund of taxes.
c) Availment of ITC on the basis of invoices for which actual supply has not been made.
d) Failure in payment of tax after collection for more than three months..
|
Section
|
Description of Offence
|
Punishment
|
|
132(1)(i)
|
Tax Evaded/ ITC Excess Claimed/ Refund wrongly taken > INR 5 Cr.
|
Imprisonment up to 5 years with fine
|
|
132(1)(ii)
|
Tax Evaded/ ITC Excess Claimed/ Refund wrongly taken > INR 2 Cr. & up to INR 5 Cr
|
Imprisonment up to 3 years with fine
|
|
132(2)
|
Conviction of person already convicted (irrespective of amount)
|
Imprisonment up to 5 years with fine
|
It is important to note that authorisation of arrest can be done only and only when the offence is among the specified category and is punishable as mentioned above. Arrest power can be used only if the proposed liability is expected to be exceeding Rs.2 crores and not otherwise.